Technique
|
Technique
Centrifuge fifteen mil of well-mixed piddle for five minutes at speed (1000 rpm), discard the supernatent portion of piddle, and re suspend the sediment.
Place a drop of re suspended sediment on a clean slide, palace a canopy put on that of piddle, and examine below microscopically at low and high power, mistreatment reduced light-weight (close the iris or lower the condenser lens).
Stains ar obtainable to be used on piddle sediment however aren't necessary.
The range of structures known ar expressed as number per high power field (HPF). This range is taken in light-weight of the piddle relative density.
|
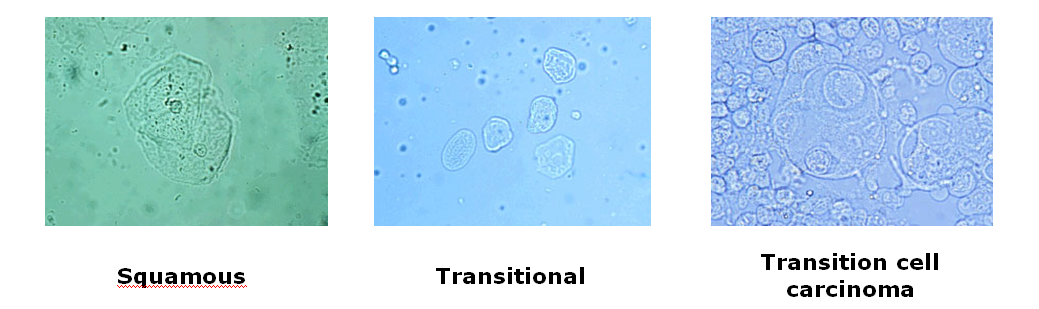
Epithelial Cells Found in Urine
Sediment
|
Squamous cells originate from the canal or prepuce and area unit thought-about contaminants. they need no pathologic significance.
Transitional cells originate from the pelvis, ureter, bladder, and epithelial duct. They exuviate naturally or throughout manipulation. they're of no pathologic significance unless they're growth (transitional cell malignant neoplastic disease within the commonest tract neoplasm)
Cells Found in Urine Sediment
|
Erythrocytes areslightly, small, slightly refractile, clear and refractile. They swell in hypotonic urine and crenate in hypertonic urine. Their presence > 2-3/HPF suggests hemorrage (hematuria) along the urinary system (or genital tract in voided samples).
Leukocytes may larger than erythrocytes like appear granular.
Occasionally their nuclei are observed.
Their presence in numbers > 2-3/HPF that suggests inflammation along the urinary tract
|
Casts
|
|
|
Casts are rectangular structures elongated composed of mucoprotein secreted by tubular epithelial cells, filtered proteins, and material available in the tubular lumen when the cast is formed.
Casts indicate tubular disease but tell you nothing about the severity of the process.
Casts formations is favored by an acidic environment. Casts dissolve in alkaline urine.
Casts are identified by their own contents, i.e., cellular casts, erythrocyte casts, Hyaline casts, fatty casts. are composed mostly of mucoprotein and are hard to visualize. Granular casts are composed of
filtered protein, mucoprotein, and tubular-cell debris. waxy are very wide, and
have square ends; otherwise they hyaline casts.
Types of Casts Found In The Urine

Organisms Found in Urine

Bacteria
and parasite ova are most often pathogens, while yeast and fungal hyphae are
usually contaminants.
|
Bacterial
rods are easy to visualize unstained, but cocci may be difficult to
distinguish from individual amorphous crystals unless they occur in chains.
Wright's staining of a dried sediment may be necessary if identification
using unstained wet-mounts is equivocal.
|
Crystals
|
Precipitation
of urinary solutes as crystals (crystalluria) depends on the solubility and
concentration of the crystalloid and the pH of the urine.
|
Therefore,
the presense of crystalluria indicates that the urine is saturated with the
particular crystalloid and is at the optimal pH for this to occur. It is not
evidence of calculi formation, nor is it usually indicative of a pathological
process. There are a few types of crystals that strongly suggest a disease
condition.
Crystals
are identified by their size, shape, color, and solubility in either acid or
alkali.
|
Unless
a crystal is one of a few known to be abnormal in urine, tedious attempts at identification
are not worthwhile.
|
Common Crystals Seen in Normal Urine
|

Triple phosphates (alkaline urine) are 6 to 8
sided prisms, calcium oxalates (acid urine) are octahedral structures,
amorphous urates (acid urine) and phosphates (alkaline urine) are fine
granules, and calcium carbonates (alkaline urine) are spheres and dumbbells an are very common in the horse
|
|








No comments
New comments are not allowed.